|
12.2.1.7 list system implementation methods
12.2.1.8 compare the advantages and disadvantages of system implementation methods
Methods of implementation of new or updated systems
Typically there involves a conversion from an old system to a new system.
There are four typical methods for installation or conversion:
Direct changeover
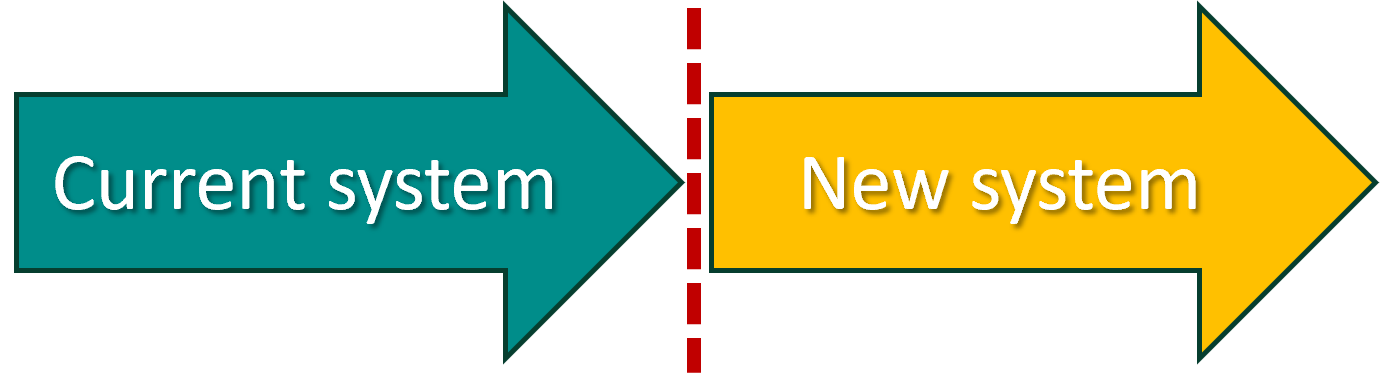
- Involves the Old system being completely dropped and the new system being completely installed at the same time;
- Need to make sure the new system is completely functional and operational;
- This conversion method is only used when it is not feasible to operate separate systems at the same time;
- Any data and training must be done before the installation.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| A new system available to everyone in the company immediately |
The riskiest method - if something goes wrong, there is nothing to fall back on. Have to wait while the problem is fixed. |
| Often the cheapest method of installation |
Have to transfer all of the data to the new one before the old one can be switched off |
| Don't need to keep duplicate sets of data |
There will be a period when no system is available because can't have the old one working while a new one is being switched on |
| |
There will be a period of upheaval while the system is brand new and staff are finding their way around it |
Parallel conversion
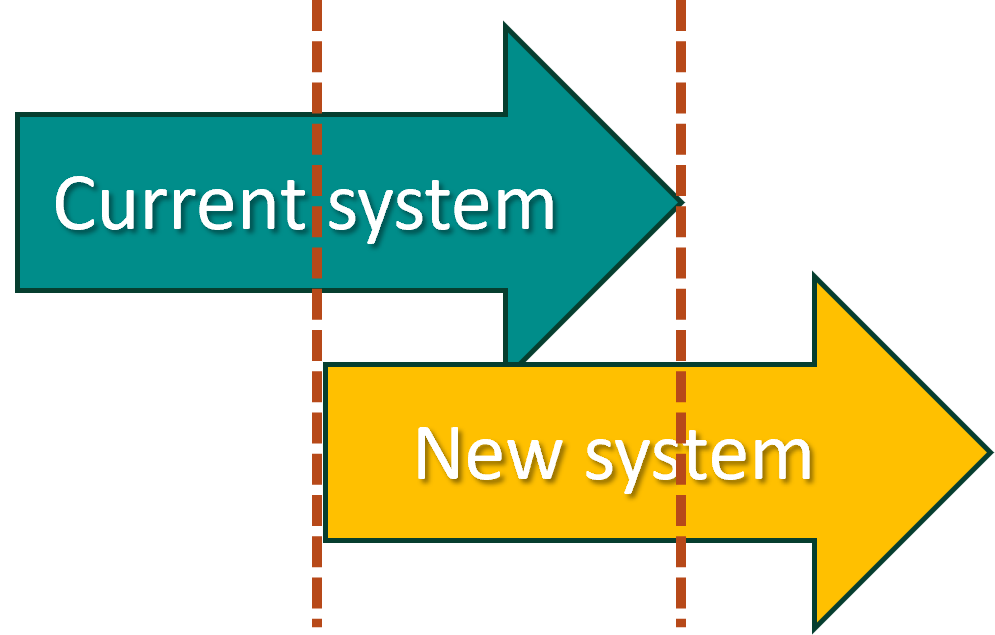
- Involves the operation of both systems for some time;
- This allows problems with the new system to be found without loss of data;
- Once the new system is fully functional and operational the old system can stop being used;
- A consequence of using this is that old versions must continue being supported until the conversion.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Less risky than the direct method. If the new system fails, the old system is still up-to-date |
Time-consuming as data has to be entered into both systems |
| Less stress for staff as they still have the security of the old system |
One system can become out of sync. with the other. |
| Staff can take their time to learn to use the new system |
Maintaining duplicate sets of data can lead to errors |
| |
The extra cost of running and maintaining two systems |
Phased conversion
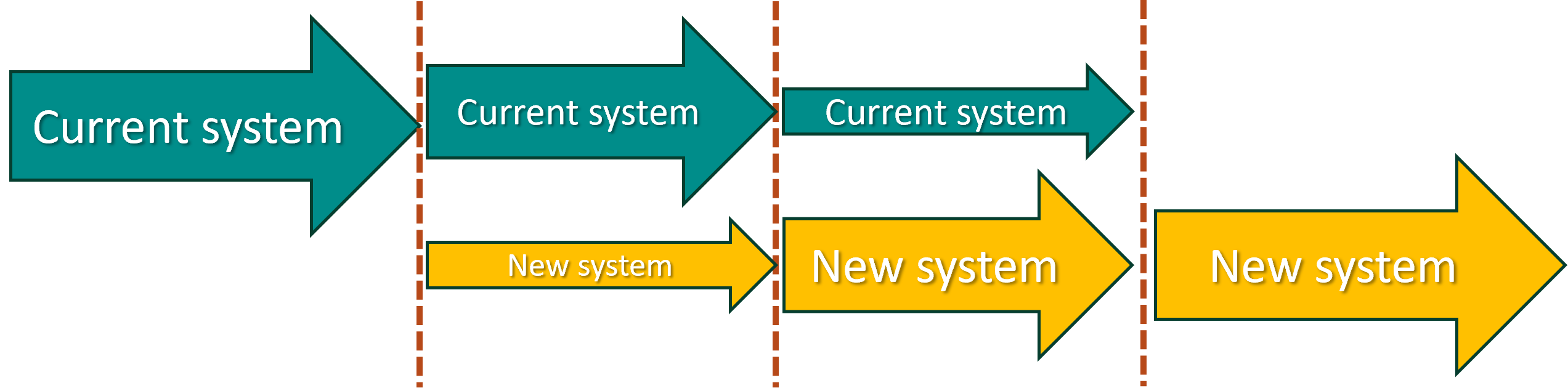
- The phased method of installation from an old system to a new one through a gradual introduction of the new and incarnation of the old;
- This is usually done by introducing new parts of a system while removing/replacing old ones;
- Often used when the product as a whole is still under development;
- Over time the entire system will be converted from old to new.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Less risk of the whole system going wrong, if something happens, it will only affect that specific part |
This method of installation can take a long period |
| Staff are introduced to the changes in small stages |
As parts of the system are used, users ask for changes which then hold up the installation of the next phase |
| |
It might be difficult to integrate the old and the new systems |
Pilot conversion
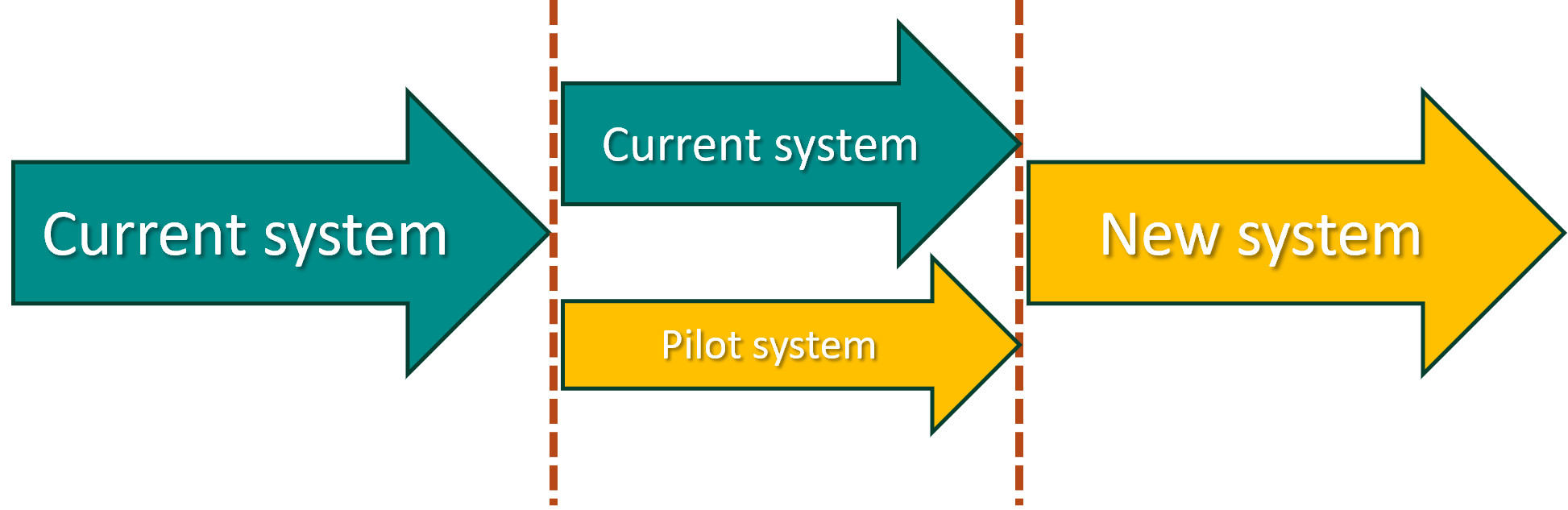
- The new system is installed for a small number of users;
- Users learn, use, and evaluate the new system;
- Once the system is seen as satisfactory the new system is installed and used by all;
- Allows users to become experts and teachers of the new system;
- Pilot conversion also allows for testing the product in an operational setting.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Only a small part of the business is affected. The rest of the business continues using the old system for now |
Even though it is only introduced to a small number of departments, those chosen will have the same disadvantages experienced as a 'direct changeover' |
| Any problems or issues are identified without affecting the whole company |
Those staff using the new system might not be able to easily share data with the rest of the company who are still on the old system |
| When the rollout happens, staff from the pilot departments can be involved in training other staff |
Extra work for IT staff who are having to support two different systems |
Sources: https://sddhsc.wordpress.com/
Questions:
1. Name four methods of new system implementation.
2. Explain the advantages of the direct method over the parallel method.
Exercises:
Ex. 1
Ex. 2
Ex. 3 (Author: Tashenova Dinara - CS teacher of NIS Uralsk)
(Goal: 2500 points)
Ex. 4 (Author: Tashenova Dinara - CS teacher of NIS Uralsk)
Exam questions:
| 


